Thats important not to confuse color gamut (color space) and color volume.
Before we deep-dive, consider this: Why does an apple appear red?
Its because it reflects red wavelengths of light while absorbing others.
Now, translate this to a TV screen.
Your TV must emit light in just the right wavelengths for accurate color representation.
But if you set the brightness to maximum, the colors will fade.
Thats because color volume depends on other factors: first of all, thats color range.
But brightness and contrast also play their role.
So the color volume is the derivative of other display parameters.
Dimensions Involved:It incorporates the range of colors (width x height) and depth (brightness).
It represents how a TV or display will reproduce colors at varying brightness levels.
This is particularly crucial for HDR content which demands precise color accuracy across diverse brightness levels.
The color gamut can be represented as red, green, and blue space.
The combinations of these primary colors create the other colors, their shades, tints, and tones.
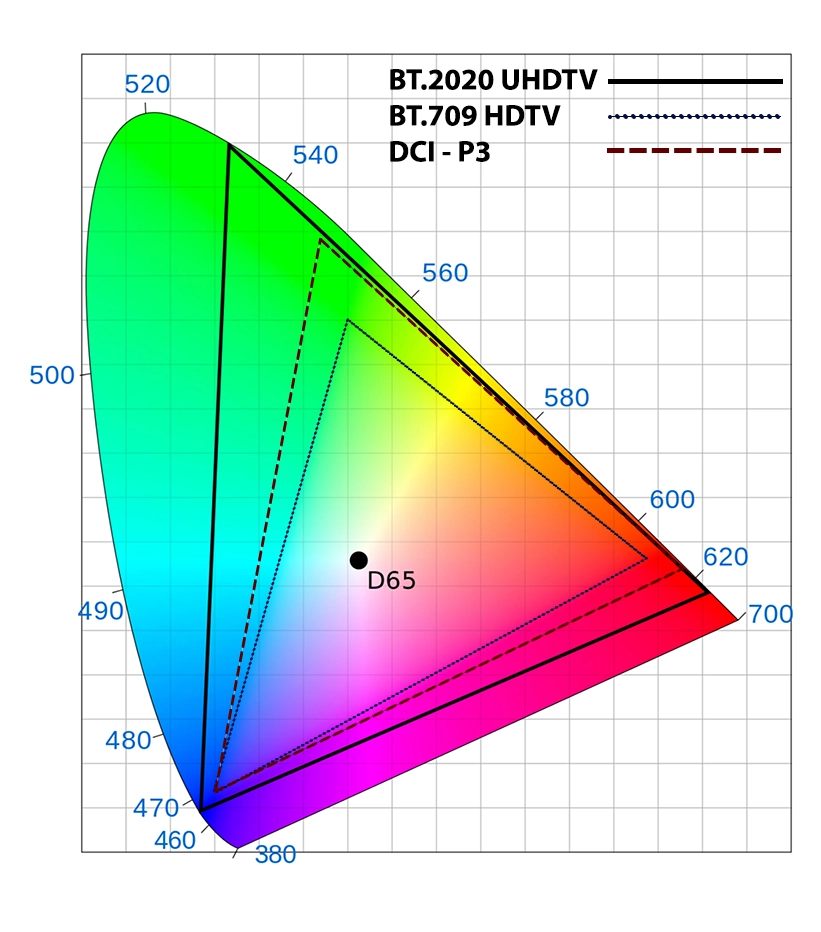
Lets take a look at this CIE 1931 color space.
It represents colors at their max saturation.
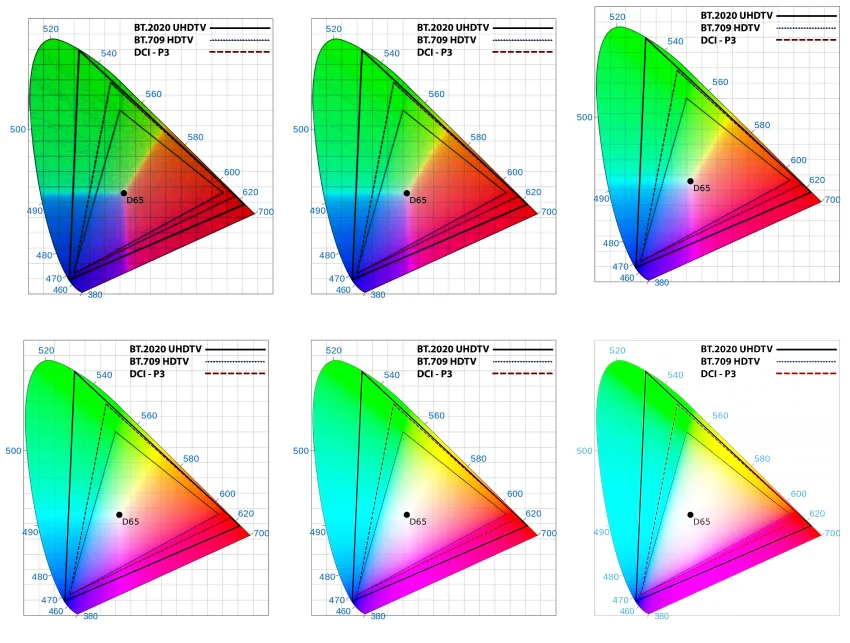
But now, lets take a look at how different luminosity levels will impact this range.
Lets take a look at how luminosity affects color volume.
Too dim, and the colors fail to pop.
Too bright, and they risk being washed out.
At high brightness levels, the image becomes bleached, losing its vibrancy and detail.
Conversely, at lower levels, the image becomes muddy.
A poor TV screen behaves that way.
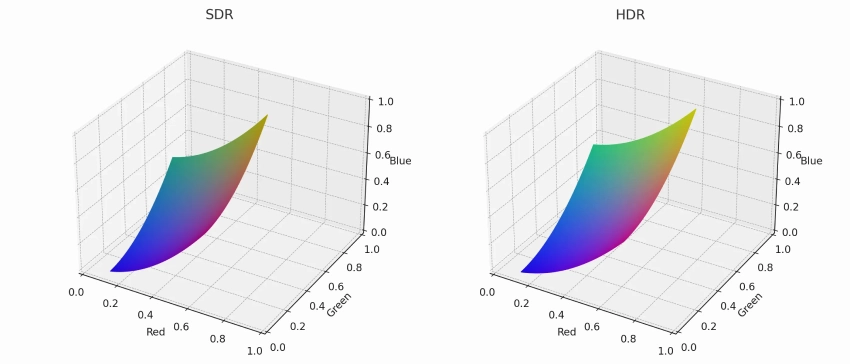
The color depth
Now, lets speak about the color depth.
Color depth isnt about the color range; thats nothing about it.
Color depth works like when youre trying to zoom out a picture.
If the size is big enough, zooming out wont result in quality loss.
Or it starts to show individual squares or pixels?
Each of those pixels has a color, right?
How rich and varied those colors can be is determined by color depth.
24-bit and 8-bit are the same.
But when it comes to the correlation between color depth and color volume, theres no direct correlation.
you might see color volume as the boundaries and the color depth as the inner filling.
This vast luminance range is the canvas upon which colors are painted.
The canvas is limited without adequate contrast, thereby compressing the color volume.
A display with low contrast will seem flat regardless of its color capabilities.
Imagine an artist with two sets of paint palettes.
The first palette has a vast range of colors, but theyre all of a similar, muted tone.
The second palette, while having the same colors, offers each shade varying levels of light and darkness.
The color volume here is fully utilized, thanks to the broader range of contrast.
Color volume and HDR
HDR and color volume a directly related.
Learn about HDR TV in detail.
In terms of color volume, LED displays can cover a decent range of colors.
However, they often struggle with deep blacks and peak brightness due to their backlighting system.
The entire panel is illuminated, leading to less precise control of individual areas of brightness.
Consequently, their ability to represent colors across varying luminance levels is good but not stellar.
A leap from LED, OLEDs emit light organically when current passes through them.
This unique property enables each pixel to emit its own light, dispensing the need for a backlight.
What does this mean for color volume?
Dramatic deep blacks, for starters, since individual pixels can be turned off completely.
OLEDs also boast a wide color gamut.
In the spectrum of color volume, they excel in showcasing vivid colors at lower brightness levels.
QLEDs are essentially LED TVs augmented with quantum dotsnano-sized semiconductor particles that dramatically enhance brightness and color.
When it comes to color volume, QLEDs shine brightly.
The pixels are made with materials that have better light transmission and color flow selectivity.
Such TVs can display an image with a depth of 10 bits.
They achieve impressive peaks of brightness, sometimes outperforming OLEDs in this arena.
As I said, color volume depends on color gamut (color space).
Theres no reason to consider Rec.
We need to change the TVs luminosity and measure the available color range on different luminosity levels.
We can express it as the % of color space that TV displays can reproduce on different luminosity levels.
Hence, independent organizations can check whether the product complies with the standard.
One such organization is the VDE Institute, which deals with product certification.