Common color depths for TVs include 8-bit and 10-bit.
you’re free to only see a difference if yourTV supports HDR.
So lets dive in!

Valeriy Odintsov
What is color depth anyway?
It is measured in bpp, bits per pixel.
256x256x256 will give us 16.7 million possible colors.
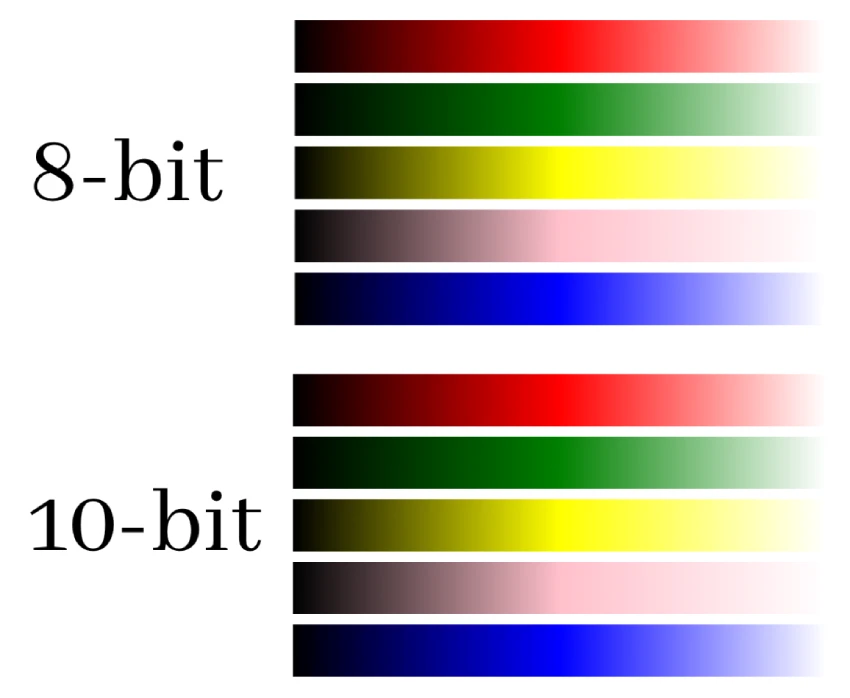
For example, each subpixel of a TV with 8-bit color depth can display 256 shades.
In turn, a 10-bit color depth TV subpixel can display 1024 shades.
It can be quite noticeable in some scenes, especially those with smooth gradients like sunsets.

But in others, it might be a tad subtler.
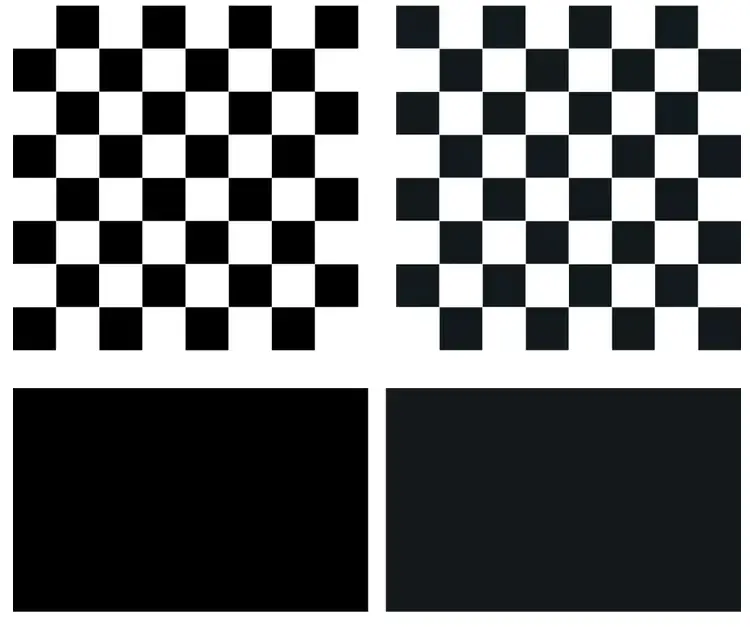
Look at the screenshot below.
As you could see, the difference between 8-bit and 10-bit is hardly noticeable.

What is color depths impact on a TV image?
The image will be displayed with the source color depth (e.g., 8-bit).
Here it’s possible for you to see the 8-bit frame in comparison to the 10-bit frame with HDR.
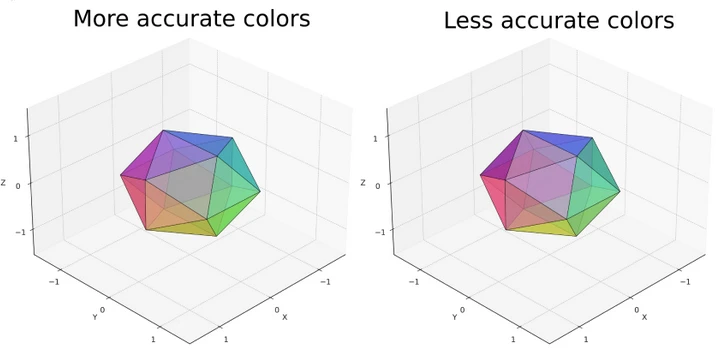
Now, lets relate this to human perception.
The human eye is estimated to distinguish between 2 to 10 million colors under typical conditions.
Bits vs.
This bit depth determines the number of possible colors that pixels can display.
Color depth is only one parameter out of dozens that affect the TV picture.
Lets look below at how color depth affects and interacts with the other parameters.

However, the smoothness of the transition between colors will not be affected.
It measures how closely the displayed colors match reference standards or original content.
A higher color depth enhances color accuracy by allowing for finer gradations of colors.
As a result, images and videos appear more true-to-life, with fewer artifacts like banding in gradients.
Its a measure of the displays ability to showcase details in an images bright and dark areas.
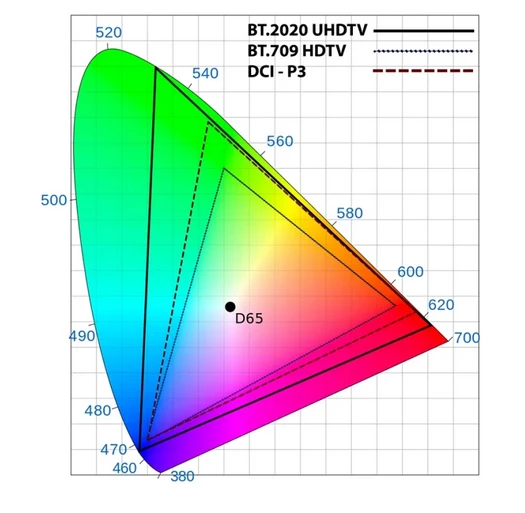
Color volume
Color volume measures the range of colors a display can produce at varying brightness levels.

Heres a color gamut (color range) in RGB format.
Do 12-bit TVs actually exist?
Today, 12-bit color technology in TVs remains more of a theoretical possibility than a reality.
Although modern LED TVs can achieve 10-bit color depth, the backlighting system can sometimes limit their color depth.
The uniformity of the backlight can affect how colors are displayed, especially in darker scenes.
To improve image quality, Samsung experimented with new quantum dot materials.
These quantum dots promised improved color reproduction and brightness compared to traditional LED materials.
This allows OLED TVs to achieve true blacks by simply turning off individual pixels.
The inherent technology of OLED screens allows for superior color depth and contrast ratios.
OLED TVs typically offer 10-bit color depth.
And turning off the pixels gives them the advantage of displaying darker shades smoother than LED TVs.
The choice between them often comes down to viewing environment, content preferences, and budget.
There are specialized test images designed to test color depth.
They look similar to the one you might see in the photo below.
This pattern shows colors transitioning from their darkest to brightest shades.
First, they look closely to see how smoothly the colors change.
However, this is a paramount view.
They point a colorimeter at the TV screen and connect it to a laptop.
Pointed at the pattern, the colorimeter captures the color values displayed on the TV.
This data is then processed by specific software, which calculates the standard deviation for each color.
The standard deviation serves as a metric to determine how closely the displayed image matches the original test pattern.
A lower standard deviation indicates a more accurate representation of the color.
A result of less than 0.12 indicates a TV with excellent color accuracy and depth.